Six Sigma

Six Sigma seeks to improve the quality of the output of a process by identifying and removing the causes of defects and minimizing variability in manufacturing and business processes. It uses a set of quality management methods, mainly empirical,statistical methods, and creates a special infrastructure of people within the organization, who are experts in these methods. Each Six Sigma project carried out within an organization follows a defined sequence of steps and has specific value targets, for example: reduce process cycle time, reduce pollution, reduce costs, increase customer satisfaction, and increase profits.
Do more with less
General Electric, pioneers in Six Sigma
 First, What is Six Sigma?
First, What is Six Sigma?
First, what it is not. It is not a secret society, a slogan or a cliche. Six Sigma is a highly disciplined process that helps us focus on developing and delivering near-perfect products and services.
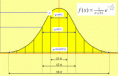
Why "Sigma"?
The word is a statistical term that measures how far a given process deviates from perfection. The central idea behind Six Sigma is that if you can measure how many "defects" you have in a process, you can systematically figure out how to eliminate them and get as close to "zero defects" as possible. To achieve Six Sigma Quality, a process must produce no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities. An "opportunity" is defined as a chance for nonconformance, or not meeting the required specifications. This means we need to be nearly flawless in executing our key processes.
· Key Concepts of Six Sigma
At its core, Six Sigma revolves around a few key concepts.
|
Critical to Quality: |
Attributes most important to the customer |
|
Defect: |
Failing to deliver what the customer wants |
|
Process |
What your process can deliver |
|
Variation: |
What the customer sees and feels |
|
Stable |
Ensuring consistent, predictable processes to improve what the customer sees and feels |
|
Design for Six |
Designing to meet customer needs and process capability |
More About 6 Sigma...
You can check more about this great project in: